Crowdsourcing and Energy Systems
Crowdsourcing, democratized marketplaces, and collaborative production are all attributes of the sharing economy. People’s drive for a self-sustainment has driven the world to this disrupting economy. By 2025, spending of the US sharing economy is projected to exceed $335 billion. The sheer Uberization of the world markets in general, and future energy systems in particular, necessitates novel crowdsourcing-based methodologies and sciences to deal with this elusive evolution. The main premise is that people in future crowdsourced energy systems will not only be willing to participate, but also committed to invest in and contribute to this ecosystem. This commitment needs to be preceded by novel energy systems designs that address the challenges associated with the transition to democratized energy systems.
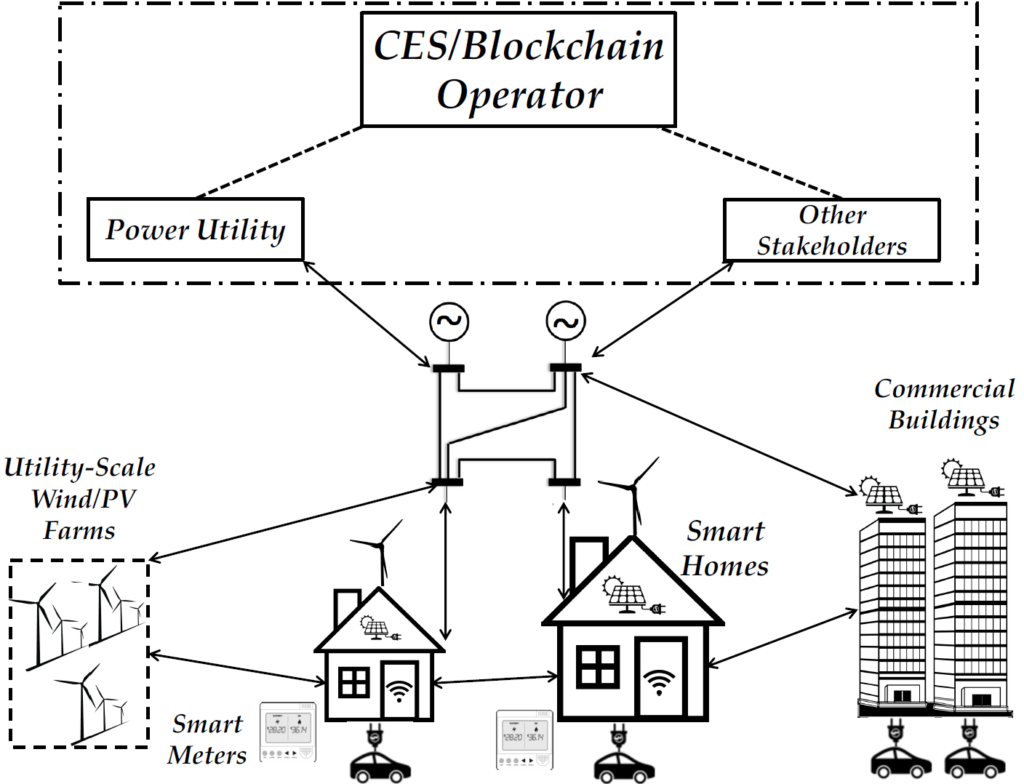
In this project, we present a high-level implementation of crowdsourcing design mechanisms for collaborative production and consumption in energy markets that are reliant on small-scale distributed generation with the assistance of cryptocurrencies and energy Blockchain (explained next). The architecture of Crowdsourced Energy Systems (CES) is shown in the below figure.
What are Blockchain and Smart Contracts? Why Energy Blockchain?
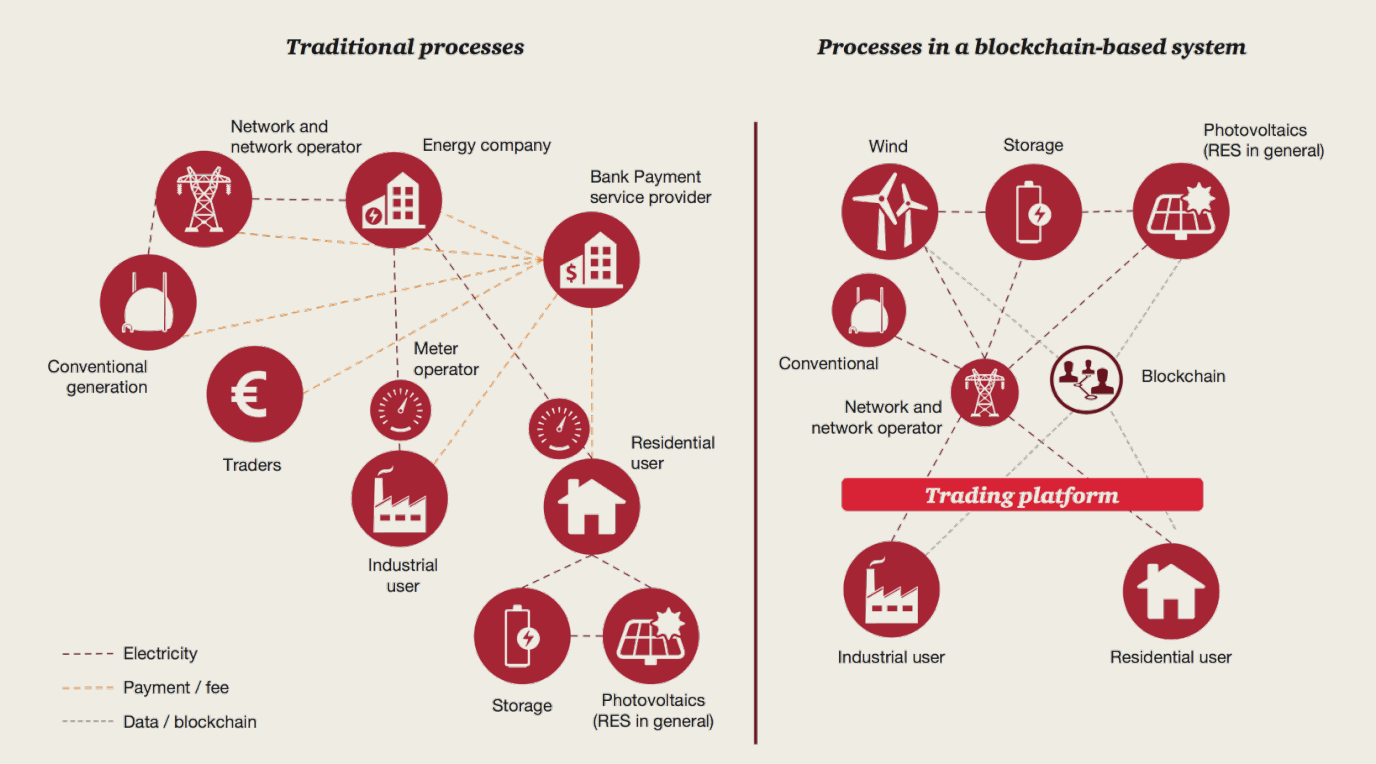
Blockchain is a distributed peer-to-peer, computational database that underlines and facilitates transactions through cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether. The main components in a Blockchain are interlinked, secure, and time-stamped blocks that define transactions between users— represented by dynamical state machines. The main motivation behind Blockchain is the need to have a distributed, secure system that eliminates the need for the so-called middle man or a central authority that organizes transactions.
Smart contracts—protocols developed to verify the performance of a contract—are a major component of Blockchain. Smart contracts and Blockchain provide an excellent platform to perform energy trading transactions. Managing the contracts through Blockchain is favored, as the system operator and local utilities have many incentives to manage the transactions via a secure, third party especially with millions of people owning distributed energy resources. The below figure shows how energy systems will evolve in the future with Blockchain-based technologies and energy trading transactions.
Project Focus
Crowdsourcing relies on the people’s open contributions to meet certain objectives and has been utilized in various cyber-physical systems and real-time markets. This research explores a framework for CESs where people sell/buy electric power in open markets, with utilities guiding these transactions. The research investigates simple dynamics-aware crowdsourcing incentives that drive the democratization of DER-reliant real-time energy markets. Such a transformation in energy systems requires a trustworthy and secure platform that manages millions of energy trading transactions. This paves the way to Blockchain-assisted CESs
Our focus in this project is two-fold. First, to develop prototype for system operators and utility companies to assist them in the management of distributed-generation-reliant energy systems. Second, to investigate computational methods that guide the future of Blockchain-assisted energy systems.